Cycle Rate Analysis for Filter Aid Selection

Filter aids are rigid, irregular shaped, non or little compactible particulate materials used as precoat or body feed to assist or enhance filtration of difficult to be filtered solid-liquid systems, such as colloidal, gel like, oily, highly viscous or highly compactible slurries or sludges. There are four principle types of filter aids: diatomaceous earth, perlite, rice hull ash, and cellulose. Each type has various size ranges or grades.
Selection of the type, grade and dosage of filter aid is based on process and process specification, cost of filter aid, and laboratory and field test and evaluation. Purity and chemical stability of filter aid material in processing environment, clarity of filtrate, filtrate flow rate, liquid product recovery, cake liquid content, easiness of cake release, and sometimes cake washing, drying efficiencies are considered in the test and evaluation.
In conventional laboratory filter aid evaluation process, assuming the filtrate quality from different grade, type or dosage of filter aids are all acceptable, the optimized selection is awarded to the one which yields the maximum amount of filtrate under certain time period, such as 20-30 minutes. However, an option with maximum filtrate amount might be associated with double cake thickness. If a cake thickness is a limiting factor for ending of a filtration cycle, with doubled cake thickness, and 1:1 filter aid to slurry solid ratio, four cycles of filtration is required to filter out a certain amount of solids, which would need one cycle to finish with no filter aid addition.
Addition of filter aid increases the filtrate flow rate, however, may lead to increased number of filtration cycles. An optimized selection should be at a point the increase offsets the additional cycles of operations. Another methodology considering cake thickness, filtration cycles, cake washing, drying, and dead time is called Cycle Rate Analysis. It gives overall cycle rate and offers a better solution for filter aid selection and optimization.
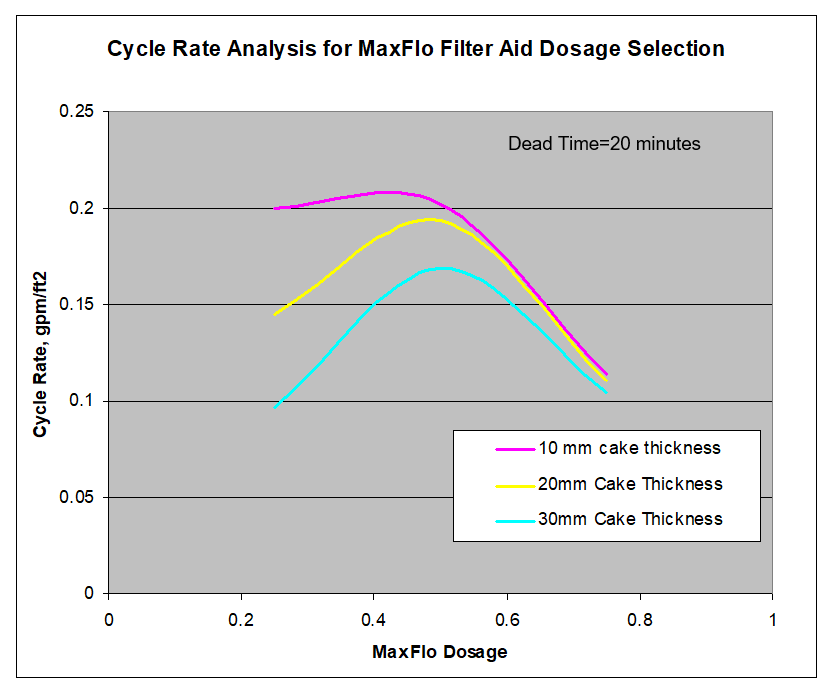
In cycle rate analysis under either constant pressure or constant rate tests, flow rate or pressure, suspension solid content, cake thickness, cake moisture content, washing and drying time, dead time, filter size are involved in the analysis. A cycle analysis result from a constant pressure lab tests of a highly compactible flocculated wastewater with MaxFlo rice hull ash filter aid is shown in Figure below. The process does not involve washing and drying, and has a typical dead time of 20 minutes. Optimized dosage occurs at the maximum cycle rate at different cake thicknesses.
Reference
Tiller, F. M., J. R. Crump, W. Chen, and Y. L. Shen, “Cycle Optimization Involving the Use of Filter Aids”, Particulate Science and Technology, 6, 243-267, 1988
Author
Wenping works for Agrilectric Research Company on rice hull ash filter aid, filtration product and technology development, and new application development.